
living below their country’s minimum wage

of Asia-Pacific youth in the labor force are unemployed in 2024

people with disabilities
Welcome to the End Austerity in Asia Pacific Virtual Data Exhibit!
Now, everyone can access the data exhibit in a virtual format. This page contains data and numbers that represent the impacts, history, and alternatives to austerity.
You can browse the entire exhibit by scrolling down or by jumping to specific sections through clicking the title beside each section. If you’re also interested in holding an in-person exhibition, you can go to the official campaign website to register, access, and print the files.
We have also prepared a new interactive generator at the end for you to try. Learn more below!
To expand the shrinking gap between a country’s revenue and debt, governments are imposing a reduction on public spending, which affects basic social services such as education, health, pension, and water. Meanwhile, debt distress in Asia Pacific continues to exacerbate existing inequalities, plunge fragile economies, and derail overall development, especially in countries which have shown a continuous rise in government debt since 2008.
International Financial Institutions (IFIs) have leveraged fiscal power to impose their interests as well as donor countries’ across development projects in the region. These aid-dependent structures inflicted on developing countries to finance development place them in a vulnerable spot, exposing Asia Pacific peoples to further marginalization through increasing taxes, cutting back social services, and poverty-inducing inflation. The perpetual imposition of aid and debt conditionalities on Southern economies influences national policies at the expense of people’s rights and sovereignty.
This data exhibit aims to raise people’s awareness on the impacts of austerity measures and mobilize them by resisting donor countries’ and international financial institutions’ interests that enable corporate control of development and of national policies, as well as pushing for alternatives.
Austerity is a macroeconomic policy aimed at reducing budget deficits by managing debts and controlling public spending, often implemented by governments during economic downturns or debt crises.
The mounting debt of countries from IFIs gives the latter the upper hand in imposing conditionalities and austerity measures on the former. Governments are forced, yet sometimes complicit, in slashing public spending, which affects subsidies and benefits for the people, to adhere to the agreement with IFIs. As a result, marginalized sectors of society are left with no choice but to endure increases in taxes and a lack of social services.
Elimination or reduction of subsidies, on fuel and energy, electricity, food products and agriculture inputs such as seeds, fertilizers and pesticides;
Wage bill cuts or caps on salaries of education, health and other public sector workers;
Rationalizing safety nets and welfare benefits via revising eligibility and further targeting to the poorest;
Pension reforms such as raising contribution rates, delaying the retirement age and lowering benefits;
Labor market reforms, specifically, restraining the minimum wage, limiting salary adjustments to cost of living standards, decentralizing collective bargaining, relaxing dismissal regulations and enabling temporary/ atypical contracts to hire workers; and
Healthcare reforms, in the form of raising fees for patients and introducing cost-cutting measures in public healthcare centers.
The introduction of new, or the expansion of already existing, consumption taxes on goods and services, like value added taxes;
The privatization of government assets and services; and
The strengthening public-private partnerships.

living below their country’s minimum wage


people with disabilities

of world’s elderly population are in Asia Pacific
2 out of 3 out-of-school children in Asia Pacific are from South Asia

of all maternal deaths in Asia Pacific occured in low and lower middle income countries in 2020
Only 43% of Asia’s citizens have access to social protection benefits
The Philippines increased its taxes by as much as 8-10% to satisfy IMF conditionalities for a $650 million loan which propelled workers in the labor market to demand a higher wage. In the same year, the national government reduced country’s budget by 5%.
The conditionalities from a 1988 IMF loan propelled the Algeria Food Crisis as the country reduced their food subsidies to 2.3% (subsidy-to-GDP ratio) from 5% ratio a year before.

Australia increased its defense spending by 47% to strengthen its alliance with the United States and its participation in international military operations despite facing budget constraints.
In Japan, 2 out of 3 low-income households relying on public assistance suffered from the 5% reduction in public benefits

 Sri Lanka faced foreign debt crisis during and post-pandemic. Increase in taxes, elimination of subsidies, and cutting public spending caused food insecurity where women were primarily affected.
Sri Lanka faced foreign debt crisis during and post-pandemic. Increase in taxes, elimination of subsidies, and cutting public spending caused food insecurity where women were primarily affected.
 1 out of 3 households were food insecure
1 out of 3 households were food insecure
 Almost 50% of children aged under 5 faced malnutrition
Almost 50% of children aged under 5 faced malnutrition 
The region continues to succumb to insurmountable debt due to conflicts, wars, economic instability, and the recent COVID-19 pandemic. IFIs remain culprits to the increasing public debt of Asia Pacific. Prevalent financing efforts intended to aid countries through loans plunge them further into a more distressing state. This visualization provides an overview of the Asia-Pacific’s debt situation. It maps out the debt-to-GDP ratio, a measurement of a country’s vulnerability to economic and political shocks as well as its ability to pay its debt, with a threshold around 60–70%.
Asia-Pacific countries* are considered Fragile and Conflict Affected Situations (FCAS)
*Afghanistan, Iraq, Lebanon, Myanmar, Syria, Palestine, Yemen, Republic of Kiribati, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Papua New Guinea, Solomon Islands, Timor-Leste, and Tuvalu
Asia Pacific countries eligible for International Monetary Fund’s Poverty Reduction and Growth Trust are classified based on risk of debt distress
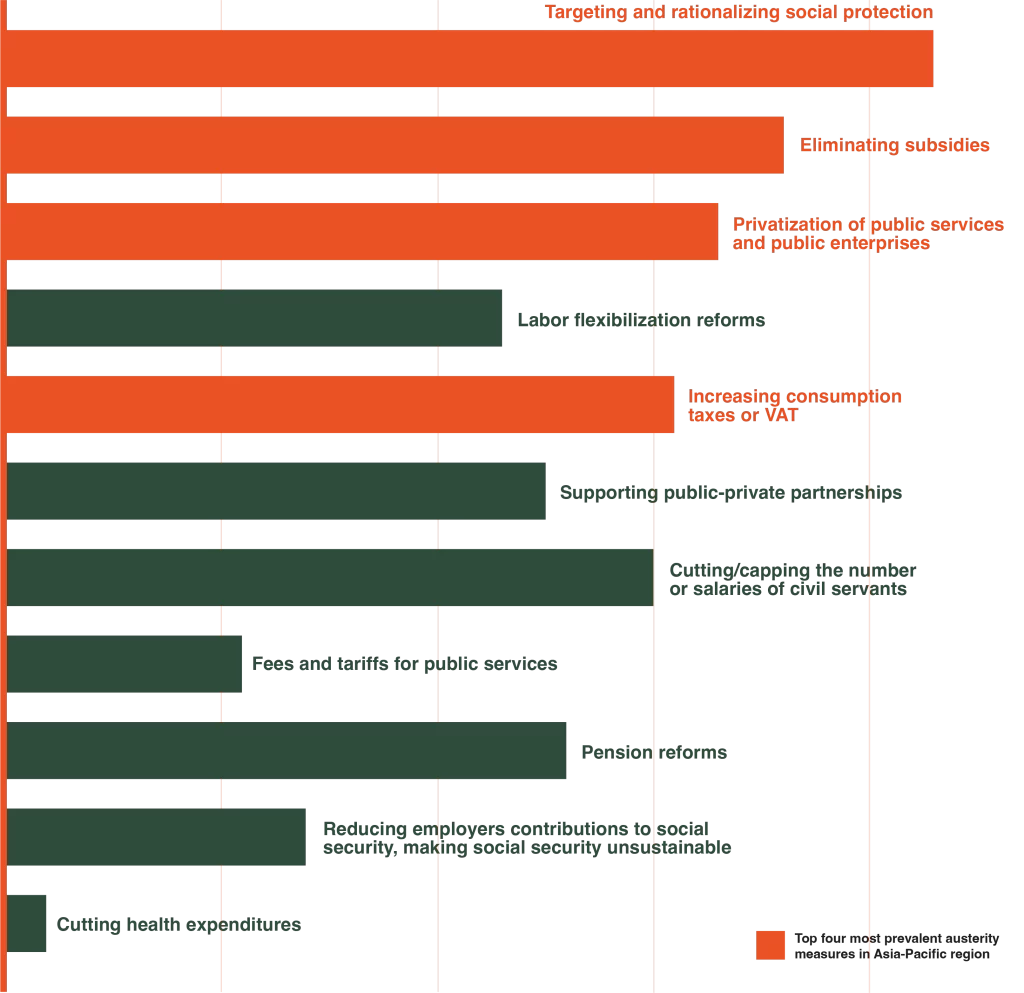
The bar graph represents the prevalence of each austerity measure in Asia Pacific countries. It attempts to show which of the austerity measures are the most prevalent through data from reports and similar campaigns. The X axis represents the number of countries implementing (or planning to implement) a particular austerity policy, while the Y axis lists down the measures.



Monopoly capitalism drives austerity as economic reform, exploiting women’s unpaid work to boost profits. It is “gendered,” making women and girls involuntary “shock absorbers” of fiscal consolidation due to power relations affecting resource distribution and care labor.
Older women:
Social security and pension cuts
Younger women and mothers:
Cuts in subsidies for education, childcare, basic services, housing, transportation, and food can push girls and single mothers out of school.
Women and girls experience those impacts differently throughout their lives, hence the importance of a life-cycle approach in addressing those impacts.

single mothers

women who live in poverty

women with disabilities

women refugees

migrant women

victims of sexual assault

women living in rural areas

women belonging to ethnic groups

young women
lesbian and intersex women

religious or linguistic minorities
WOMEN AND AUSTERITY IN NUMBERS
in Asia Pacific planned to cut their social protection budget for maternity and childcare coverage in 2023
in Asia Pacific have below 50% maternity care coverage
At least
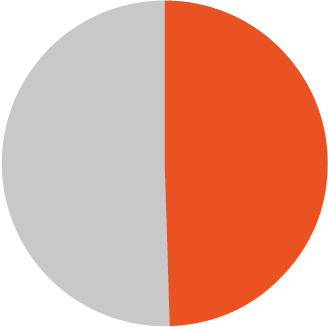
increase in poverty rate as women faced double the care work at 95% food inflation peak
A labor flexibilization reform involves adjusting labor laws and practices to better adapt to economic and market changes. This typically includes favoring contractualization over regularization and adjusting wages and working hours, which can affect workers’ job security and their ability to unionize.Evidence shows that these labor flexibilization reforms generate precarization instead of jobs, depress domestic incomes and in the end, aggregate demand, which also hinder economic recovery.
GLOBAL DATA: LABOR IN NUMBERS
Only about
of global workers are wage and salaried employees
workers are in informal employment, most of which without social protection
workers live in extreme or moderate poverty worldwide and around
workers are unemployed

workers live in extreme or moderate poverty worldwide and around
workers are unemployed
ASIA PACIFIC DATA
In March 2021, the International Monetary Fund had supported the plans of 31 countries to reform their public wage bill, six of which were from the Asia Pacific region.


Austerity does not cause employment-generating growth. In the short term, austerity depresses incomes and hinders domestic demand, harming economic activity and employment and ultimately undermining recovery efforts. In the long term, as unemployment and excess capacity persist, potential output tends to decrease.

Essentially, austerity undermines the right to work with its erosion of other fundamental rights; its restraining of minimum living wages; its weakening of collective bargaining; and its push to cut on universal social protection.
The International Monetary Fund, or IMF, has been notorious for imposing austerity policies, which is just another ploy to sustain neoliberal objectives that prioritize free markets over tackling and addressing major socio-economic crises plaguing the region.
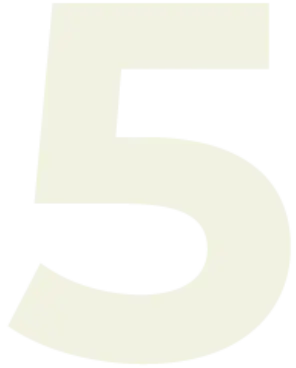

“For every $1 the IMF encouraged a set of poor countries to spend on public goods, it has told them to cut four times more through austerity measure.” -Oxfam International
IMF CURSE ON SRI LANKA
 Half of the Sri Lankan population suffered from multiple vulnerabilities due to IMF-imposed austerity measures through their government
Half of the Sri Lankan population suffered from multiple vulnerabilities due to IMF-imposed austerity measures through their government
food inflation peak
poverty rate (doubled from 13.1%)
worth of extended arrangement over 48 months
Interest rates DOUBLED Subsidies ELIMINATED Public spending SLASHED
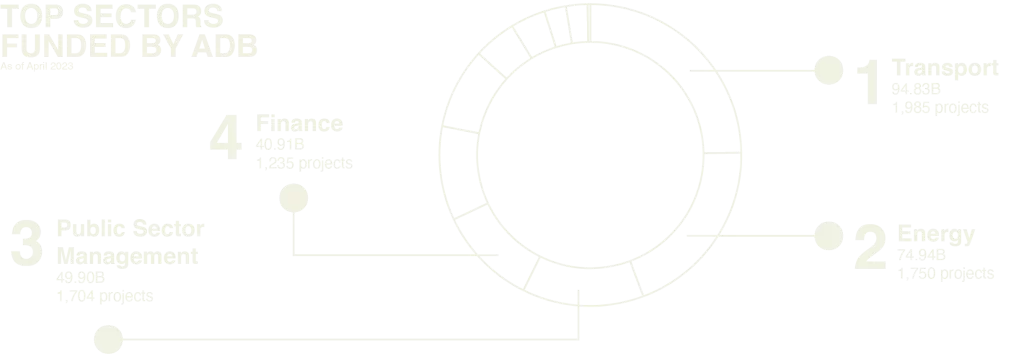
The data shows the bank’s role in fiscal management and the policies of their developing member countries. In the bank’s project dataset from 2005-2023, over 50 projects worth USD 3 billion were found dealing with fiscal reforms, fiscal management, fiscal governance, debt management, etc.

SOVEREIGN PROJECTS
under public expenditure and fiscal management subsector from 2005-2023
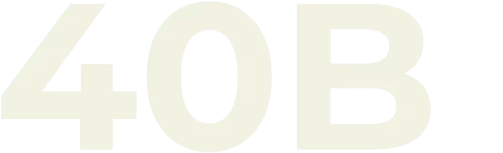
TOTAL PROJECT COST
in Asia Pacific under finance sector with over 1,235 projects







Your budget will be coming from the total military expenditures of the specific sub-region you selected. Click “Next” to proceed.

your region's budget

Got questions?
Send your inquiry to endausterity@realityofaid.org.
To access the references of this data exhibit, click here.